Low-code development combines the best of both worlds in a single platform where both non-technical users and professional developers can apply their skillsets, collaborate, and co-develop solutions.
Low-code is an application development method that elevates coding from textual to visual.
Rather than a technical coding environment, low-code operates in a model-driven, drag-and-drop interface. All development skill levels — professional developers, novice developers, subject matter experts, business stakeholders, and decision makers — can use low-code to build value-driven enterprise business applications.
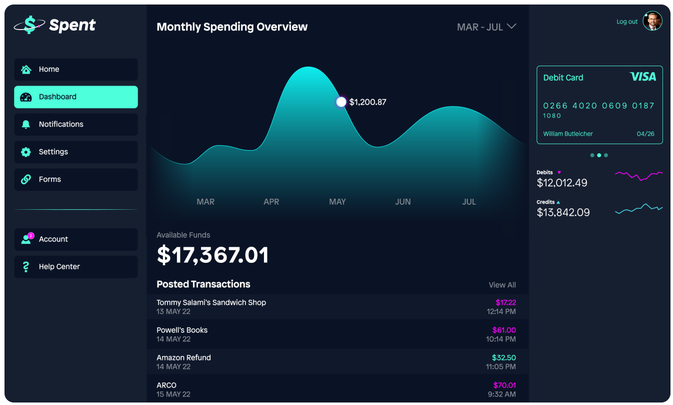
Low-code application development platforms (LCAPs) abstract and automate every step of the application lifecycle. Development is more accessible to users without technical expertise, with features that accelerate the development process.
Drag-and-drop functionality and an intuitive visual UI make it possible for professional developers to increase their productivity and for citizen developers to build all types of apps. Model-driven development lets you visualize how the app works as it’s being built with the ability to launch with one-click deployment.
Build cross-platform apps with pre-configured modules, logic, templates, connectors, and more. Components of a low-code app can be customized and extended by skilled developers.
Develop collaboratively with built-in tools for feedback loops, revision tracking, user stories, messaging, and more. The visual nature of low-code keeps everyone speaking the same development language.
Deploy new apps and augment existing apps quickly as customer demands and business needs change. A cloud-based low-code platform provides flexibility, support for continuous delivery, and run-time and dev-time scalability on demand.
Securely integrate data and logic from any source, system, or service — including your core legacy systems. Build apps using pre-configured APIs and connectors, or empower your skilled developers to build a custom integration.
Low-code supports all phases of the app development lifecycle with tools to streamline project management, requirements management, version control, testing, deployment, and more. Holistic low-code platforms incorporate Agile development practices and DevOps tools.
What is the difference between low-code and…
No-code development is ideal for people with no coding knowledge or experience. With this development technique, you can build basic apps with a limited scope, without involving IT.
Features of no-code:
![]() Simple, visual development environment
Simple, visual development environment
![]() Limited customizations and integrations
Limited customizations and integrations
![]() Not suited for legacy system overhauls
Not suited for legacy system overhauls
High-code, or traditional development, involves manual coding in multiple languages with various technologies. You can build any solution, but you’ll be heavily reliant on professional developer resources.
Features of high-code:
![]() Specialized skillsets with a small talent pool
Specialized skillsets with a small talent pool
![]() Time-intensive and costly
Time-intensive and costly
![]() Need to develop separately for mobile, web, and various operating systems/devices
Need to develop separately for mobile, web, and various operating systems/devices
No-code development is ideal for people with no coding knowledge or experience. With this development technique, you can build basic apps with a limited scope, without involving IT.
Features of no-code:
![]() Simple, visual development environment
Simple, visual development environment
![]() Limited customizations and integrations
Limited customizations and integrations
![]() Not suited for legacy system overhauls
Not suited for legacy system overhauls
High-code, or traditional development, involves manual coding in multiple languages with various technologies. You can build any solution, but you’ll be heavily reliant on professional developer resources.
Features of high-code:
![]() Specialized skillsets with a small talent pool
Specialized skillsets with a small talent pool
![]() Time-intensive and costly
Time-intensive and costly
![]() Need to develop separately for mobile, web, and various operating systems/devices
Need to develop separately for mobile, web, and various operating systems/devices
Low-code development combines the best of both worlds in a single platform where both non-technical users and professional developers can apply their skillsets, collaborate, and co-develop solutions.
With separate integrated development environments (IDEs) catered to both business users and professional developers, anyone with an idea can use low-code to tackle today’s business challenges.
Low-code provides developers with a dedicated IDE and a sophisticated toolbox tailored to support client-side, server-side, and integration development.
With low-code, professional developers can extend apps with custom code, integrate data from multiple sources, build mobile apps, leverage microservices, and translate business needs into custom solutions.
Rather than wait for IT, non-technical business users can use low-code’s simplified development environment to build their own apps.
Governance cuts down on shadow IT and empowers anyone to build basic apps while IT still maintains visibility and control of the organization’s app landscape.
Low-code provides developers with a dedicated IDE and a sophisticated toolbox tailored to support client-side, server-side, and integration development.
With low-code, professional developers can extend apps with custom code, integrate data from multiple sources, build mobile apps, leverage microservices, and translate business needs into custom solutions.
Rather than wait for IT, non-technical business users can use low-code’s simplified development environment to build their own apps.
Governance cuts down on shadow IT and empowers anyone to build basic apps while IT still maintains visibility and control of the organization’s app landscape.
How do you choose the right low-code development platform when there are more than 300 vendors in the market? At its foundation, your low-code platform should be equipped to help you meet the ever-increasing demand for software solutions. But what about the details? Every low-code development platform is different. Use the evaluation criteria below as you’re vetting your options.
To empower your entire workforce to co-create solutions, make sure the platform you use has separate IDEs for both professional and citizen developers. The platform should have built-in tools to facilitate real-time collaboration between business and IT throughout the application lifecycle.
Organizations have vast amounts of data across various teams. The platform should have the ability to integrate with any system and data source. Your low-code platform should make it easy for developers to find, understand, and use data from any internal or external source — without compromising data security.
Your low-code platform should have an integrated set of tools and services for continuous support throughout the application development lifecycle — from ideation and requirements gathering to deployment and performance management. This support eliminates the traditional bottlenecks, costs, and risks associated with app delivery while increasing quality and providing a better development experience for all stakeholders involved.
End-users expect frictionless experiences across their various devices. Your low-code platform should offer development and operational support for web, mobile, immersive, and conversational experiences to optimize UX.
To support developers of all skillsets, the platform should offer a no-code IDE with drag-and-drop widgets, reusable components, and real-time collaboration tools to enhance citizen development productivity. The platform should also include a sophisticated low-code IDE with flexible integration and extensibility, as well as out-of-the-box DevOps tools to help professional developers build complex apps and systems faster.
Your low-code platform should support the scalable development of cloud-native apps with the option to deploy on public, private, or hybrid clouds, as well as on-premise.
From a departmental level to the entire enterprise, low-code is helping organizations across the globe revolutionize the way they solve business problems.
Push your digital strategies forward by building and innovating solutions quickly that drive unprecedented business value.
Low-code is the future of application development— and it has the reputation to prove it.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |